
Teleradiology: The Here & Now
Modern healthcare has seen a remarkable advancement in radiology services, particularly in the form of teleradiology. Teleradiology plays a...
A Complete Guide to Selecting the Right PACS Model:
The field of medical imaging is ever evolving, and with it, the technologies that drive its progress. At the heart of this evolution lies Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), playing a pivotal role in storing, retrieving, presenting, and sharing medical images. As we advance further into the digital age, the deployment of PACS comes in various formats: traditional on-premises setups, cloud-based solutions, and hybrid models. Each format offers distinct advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for specific scenarios. Understanding the nuances between these architectures has become crucial to optimizing efficiency, safeguarding patient data, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
This article intends to offer in-depth comparisons of on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid PACS models. We assess elements including affordability, security, scalability, data accessibility, and flexibility. Our mission is to support healthcare executives, IT specialists, and physicians in making well-informed decisions that align with the demands and long-term goals of their organizations. To achieve this, we provide an unbiased analysis showing no preference for any PACS deployment options. Our goal is to present a transparent evaluation by weighing the advantages, disadvantages, and potential challenges associated with each option. By doing so, we hope to empower our readers with the necessary knowledge to make the best PACS model choice for their specific healthcare institution.
By delving into each model's distinctive features, we aim to stimulate a discourse that will guide future PACS deployment strategies in an increasingly digital, patient-centric healthcare landscape. The narrative of this article underscores that there is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to PACS; instead, the optimal solution depends heavily on the specific goals, resources, and constraints inherent to each healthcare institution.
Onsite PACS are PACS installed on-site, within the premises of a healthcare facility. They consist of hardware components such as servers, storage devices, and workstations, as well as software components like image management software and viewing applications. Onsite PACS are typically managed and maintained by the IT staff of the healthcare facility. Here are several benefits of onsite PACS:

On-premise PACS, though often preferred for the level of control and potential customization they offer, can come with a series of disadvantages that organizations need to carefully consider.
Cloud PACS
Cloud PACS are PACS hosted on remote servers, typically in a data center. Medical images are uploaded to the cloud and accessed using a web-based viewer. Here are some of the benefits of cloud PACS:
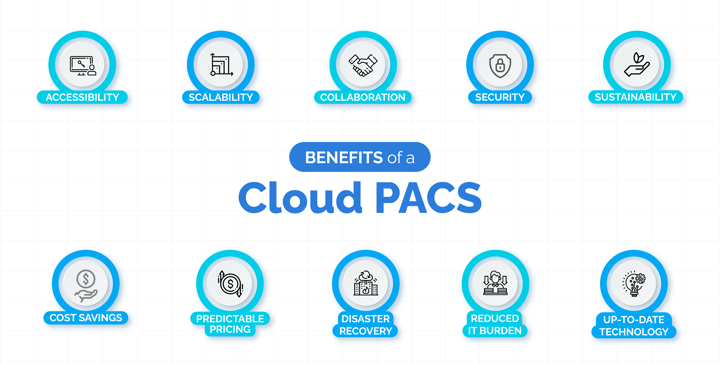
Here are 10 potential disadvantages of a Cloud PACS:
In summary, the comparison between onsite PACS and cloud PACS underscores their respective merits within the field of radiology. With rapid image retrieval, heightened security, and tailored configurations, onsite PACS offers distinct advantages. Conversely, cloud PACS deliver enhanced accessibility, scalability, and economic viability. Deciding between these two hinges on the distinct requisites and assets of the healthcare establishment; cloud PACS might emerge as the prudent choice for resource-constrained facilities, whereas onsite PACS could be favored by those placing a premium on security protocols.
The last model to examine is the Hybrid model, where a server is placed both onsite and offsite. Hybrid model is typically configured as a Cache onsite and cloud server where there is unidirectional communication. It can also be configured to have identical servers onsite and in the cloud. These servers are configured to communicate asynchronously in real time. When the hybrid model runs asynchronously and the cache model uses unidirectional replication, the way data is stored, processed, and synchronized between the servers will change. Let us discuss how these changes affect each model:
Asynchronous Hybrid Server Model is when the hybrid model runs asynchronously, it means that data is updated between the cloud server and the onsite server at different times, without waiting for an immediate response from the other server. This can lead to temporary inconsistencies between the two servers, but they will eventually synchronize.
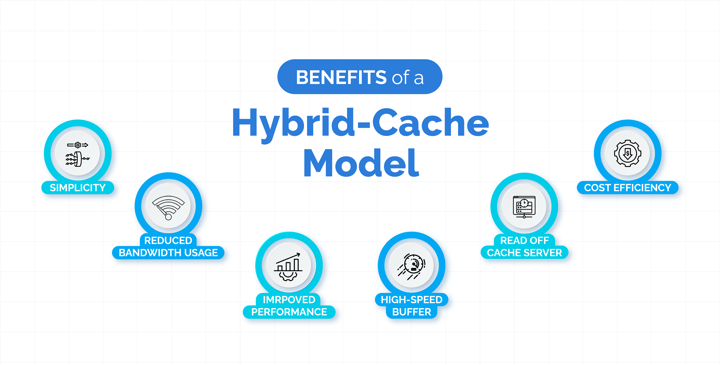
Hybrid-Cache Model
Advantages:
Hybrid-Asynchronous Model
A Hybrid-Asynchronous Model for a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) represents a unique blend of on-premise and cloud-based storage systems, attempting to bring together the best of both worlds.
In this model, part of the data storage and management occurs on local servers (on-premise) and part on a cloud-based server. The specific division between on-premise and cloud storage can vary based on the needs and preferences of the organization. It involves keeping frequently accessed or particularly sensitive data on-premise while less frequently accessed data is stored in the cloud.
The term "asynchronous" in this context usually refers to how data is transferred and synchronized between the on-premise and cloud-based components of the system. Rather than simultaneously updating data in both locations (a synchronous approach), an asynchronous model updates the data at different times. This could be done based on a schedule or specific triggers, such as when data reaches a certain age or has not been accessed for a specified period.
The Hybrid-Asynchronous Model can provide increased flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to a purely on-premise or cloud-based PACS. By keeping frequently accessed data on-premise, organizations can ensure fast, reliable access to that data, while also benefiting from the broader accessibility and scalability of cloud storage.
However, this model also comes with its own challenges. It can be more complex to manage and secure, and it requires careful planning and coordination to ensure that data remains synchronized and accessible when needed. As with any technology decision, healthcare organizations must weigh these factors against their specific needs, resources, and strategic objectives when considering a Hybrid-Asynchronous Model for PACS.

While the Hybrid-Asynchronous Model for PACS presents numerous benefits, it is equally important to consider the potential challenges. Here are 10 possible disadvantages to this approach:

In conclusion, the selection between onsite PACS and cloud PACS is intricately tied to the unique requirements and available resources of each healthcare facility. Therefore, it is essential that healthcare providers tailor their PACS implementation plan to fit their unique needs and be aware of the potential for technological disruption and costs associated with PACS.
Common Myths
Common myths associated with onsite PACS, Cloud PACS, and hybrid models in healthcare imaging management often revolve around misconceptions regarding their functionality, security, implementation and compliance. Below are some of the most common Myths about each PACS model:
All PACS are made the same: While PACS systems share a common purpose of managing medical images, they are not all made the same. Healthcare organizations must carefully evaluate their requirements, conduct thorough research, and consider factors such as features, integration capabilities, scalability, support, and regulatory compliance when selecting a PACS solution that best fits their needs.
You need AI to operate at peak performance: AI can offer significant benefits for PACS systems, it is not a prerequisite for PACS to operate at peak performance. Healthcare organizations should carefully evaluate their needs, consider the potential benefits and challenges of AI integration, and explore alternative solutions to optimize PACS functionality and performance based on their specific requirements.
Even Cloud deployments require hardware to be deployed onsite: There are many vendors who prefer that you add an onsite appliance that will send your DICOM to their cloud. In this method your data is encrypted through TLS. In many instances there is an additional monthly charge for the software, it also means the vendor does not need to build or maintain any VPNs. Sending from any site to a cloud through a VPN secures transmission and eliminates the need for any onsite hardware.
You can only deploy an HL7 (ORM/ORU) if have an onsite deployment: You can deploy an HL7 regardless of PACS location. Regardless of how you have your architecture it is important to connect to your vendors early to ensure compatibility and costs.
Cloud PACS are not secure: Cloud PACS providers use a variety of security measures to protect patient data, including encryption, access control, and audit logging. In fact, cloud PACS are often more secure than traditional on-premises PACS, which can be vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Cloud PACS are too expensive: Cloud PACS pricing has become increasingly competitive in recent years, and there are now several affordable options available. Additionally, cloud PACS can help organizations to save money on IT costs, such as hardware maintenance and software upgrades.
Cloud PACS are difficult to use: Cloud PACS are designed to be user-friendly, even for users with no prior experience with medical imaging systems. Most cloud PACS providers also offer comprehensive training and support to help users get started.
Cloud PACS are not reliable: Cloud PACS providers offer high levels of uptime and reliability. Additionally, cloud PACS are typically backed up by multiple data centers, so that data is not lost in the event of a disaster.
Cloud PACS are not scalable: Cloud PACS are highly scalable and can be easily scaled up or down to meet the needs of your organization. This can be especially beneficial for organizations that are experiencing rapid growth.
Cloud PACS are not HIPAA compliant: Cloud PACS providers must comply with HIPAA regulations to protect patient data. Additionally, many cloud PACS providers offer HIPAA compliance services to help organizations meet their HIPAA requirements.
Cloud PACS are not suitable for all organizations: Cloud PACS are suitable for organizations of all sizes, from small practices to large hospitals. In fact, cloud PACS can be especially beneficial for small practices, as they can help to reduce IT costs and improve efficiency.
Cloud PACS are a new technology: Cloud PACS have been around for over a decade and are now a mature and well-established technology. Many healthcare organizations have already successfully transitioned to cloud PACS.
On-site PACS are more secure than cloud-based PACS: While on-site PACS can be secure, they are also vulnerable to cyberattacks. In fact, on-site PACS have been the target of a number of high-profile cyberattacks in recent years. On the other hand, cloud-based PACS providers use a variety of security measures to protect patient data, including encryption, access control, and audit logging. Additionally, cloud-based PACS are typically backed up by multiple data centers, so that data is not lost in the event of a disaster.
On-site PACS are more reliable than cloud-based PACS: On-site PACS can be reliable, but they are also susceptible to hardware failures and other disruptions. Cloud-based PACS, on the other hand, offer high levels of uptime and reliability. Additionally, cloud-based PACS providers have teams of experts who are constantly monitoring and maintaining their systems.
On-site PACS are more scalable than cloud-based PACS: On-site PACS can be difficult and expensive to scale. Cloud-based PACS, on the other hand, are highly scalable and can be easily scaled up or down to meet the needs of your organization. This is especially beneficial for organizations that are experiencing rapid growth.
On-site PACS are more cost-effective than cloud-based PACS: On-site PACS can be expensive to purchase and maintain. Cloud-based PACS, on the other hand, are typically more affordable, and can be paid for on a subscription basis. Additionally, cloud-based PACS can help organizations to save money on IT costs, such as hardware maintenance and software upgrades.
On-site PACS are more user-friendly than cloud-based PACS: On-site PACS can be complex and difficult to use, even for experienced users. Cloud-based PACS, on the other hand, are designed to be user-friendly, even for users with no prior experience with medical imaging systems. Additionally, cloud-based PACS providers offer comprehensive training and support to help users get started.
On-site PACS are more suitable for all organizations: Cloud-based PACS are suitable for organizations of all sizes, from small practices to large hospitals. On-site PACS, on the other hand, can be especially expensive and complex for small practices to manage.
Hybrid PACS models are too complex: Hybrid PACS models can be more complex to implement and manage than traditional on-site or cloud-based PACS. However, there are a number of vendors that offer hybrid PACS solutions that are designed to be easy to implement and manage. Additionally, these vendors offer comprehensive support to help users get started and keep their systems running smoothly.
Hybrid PACS models are not secure: Hybrid PACS models can be just as secure as traditional on-site or cloud-based PACS. In fact, some hybrid PACS solutions offer enhanced security features, such as multi-factor authentication and data encryption. Additionally, hybrid PACS models allow organizations to store their most sensitive data on-site, while still having the flexibility to access their data from anywhere in the world.
Hybrid PACS models are not scalable: Hybrid PACS models are highly scalable and can be easily scaled up or down to meet the needs of your organization. This is especially beneficial for organizations that are experiencing rapid growth.
Hybrid PACS models are not cost-effective: Hybrid PACS models can be more cost-effective than traditional on-site or cloud-based PACS, especially for organizations that have a large volume of data to store and manage. Hybrid PACS models also allow organizations to save money on IT costs, such as hardware maintenance and software upgrades.
Hybrid PACS models are only suitable for large organizations: Hybrid PACS models are suitable for organizations of all sizes, from small practices to large hospitals. In fact, hybrid PACS can be especially beneficial for small practices, as they can help to reduce IT costs and improve efficiency.

Teleradiology: The Here & Now
Modern healthcare has seen a remarkable advancement in radiology services, particularly in the form of teleradiology. Teleradiology plays a...

The Future of Radiology
Radiologists today face an overwhelming workload—rising imaging volumes, increasing complexity, and growing pressure to deliver fast, accurate...